How to Check?
Mengneng Coating Academy introduces various methods for testing the quality of coating films. Coating inspection is crucial in the application process as it directly affects the quality of the coating and the application results. Using professional testing tools, key indicators such as coating thickness, gloss, and adhesion can be accurately assessed to ensure that the coating meets design and performance requirements. A coating thickness gauge can prevent the coating from being too thin or too thick, while a gloss meter ensures that the surface effect meets standards. Adhesion tests help avoid issues such as coating peeling. Additionally, testing tools can verify the drying time, weather resistance, and other properties of the coating, ensuring its stability in different environments. In short, coating inspection tools are an effective means of ensuring application quality and improving coating performance.



-
-
How to detect the quality of the coating film?
The quality of the coating must ultimately reflect the quality of the coating film. Therefore, post-coating quality testing mainly involves testing the properties of the coating film, including mechanical properties (such as adhesion, flexibility, impact strength, hardness, gloss, etc.) and special protective properties (such as weather resistance, acid and alkali resistance, oil resistance, etc.). Among these, mechanical properties are essential basic routine tests in coating quality detection, while special protective properties can be selectively tested based on different usage requirements. Quality detection after coating is the final basis for evaluating coating quality and an important step in ensuring quality. The standard testing methods for post-coating quality detection are as follows.
Among these tests, users should prepare standard test samples according to the general coating film preparation method mentioned in the previous section, to test the most common mechanical and physical properties of the coating film to evaluate the basic performance.
Sample Preparation
1. GB/T 3186-82(89) Sampling of coating products
2. GB/T 1727-92 General preparation method for coating films
3. GB/T 1736-79(89) Preparation method for insulating coating films
4. GB/T 1765-79 Method for preparing coating films to test resistance to humidity, salt fog, and artificial accelerated weathering
5. GB/T 6741-86 Uniform coating film preparation method (rotary coating method)
6. GB/T 9271-88 Standard test panels for colored paints and varnishes
Condition Adjustment
7. GB/T 9278-88 Condition adjustment and test temperature and humidity for coating samples
8. GB/T 12336-90 Statistical analysis standard method for corrosion numbers
9. GB/T 12609-80 Inspection procedures for electrodeposited metal coatings and related precision coating sampling
Conversion Coating
10. GB/T 9792-88 Determination of coating mass per unit area for conversion coatings on metals (weight method)
11. GB/T 9791-88 Test methods for chromate conversion coatings on zinc and cadmium
Usability
12. GB/T 1723-93 Viscosity determination method for coatings
13. GB/T 1758-79(89) Coating consumption measurement method
14. GB/T 6753.3-86 Coating storage stability test method
15. GB/T 6753.6-86 Large area brushing test for coating products
Drying Time
16. GB/T 1728-79(89) Method for determining the drying time of coating films and putty films
17. GB/T 1762-80(89) Method for determining the tackiness of coating films
18. GB/T 6753.2-86 Small glass ball method for surface drying test of coatings
19. GB/T 9273-88 Coating film no mark test
20. GB/T 9280-88 Colored paints and varnishes stackability test
Flow Property
21. GB/T 1750-79(89) Method for determining the flow properties of coatings
22. JB/T 3998-85 Coating flow property scraping method
23. GB/T 9264-88 Determination of sagging properties of colored paints
Opacity
24. GB/T 1726-79(89) Method for determining the hiding power of coatings
25. GB/T 13452.3-92 Colored paints and varnishes opacity measurement – Part 1: For white and light-colored paints, Kubel-Munk method
26. GB/T 9270-88 Determination of opacity ratio for light-colored paints (polyester film method)
Color
27. GB/T 3181-1995 Standard for coating film colors
28. GB/T 6749-1997 Coating film color representation method
29. GB/T 9761-88 Visual color matching for colored paints and varnishes
30. GB/T 11186.1-89 Measurement method for coating film color – Part 1: Principles
31. GB/T 11186.2-89 Measurement method for coating film color – Part 2: Color measurement
32. GB/T 11186.3-89 Measurement method for coating film color – Part 3: Color difference measurement
33. GSB G51001-94 Standard color samples for coating films (physical standard)
Thickness
34. GB/T 1764-79(89) Method for determining coating film thickness
35. GB/T 4956-85 Magnetic method for measuring non-magnetic coating thickness on magnetic metal substrates
36. GB/T 6462-86 Microscopic method for measuring cross-sectional thickness of metal and oxide coatings
37. GB/T 6463-86 Thickness measurement method review for metal and other inorganic coatings
38. GB/T 11378-89 Thickness profile measurement method for metal coatings
39. GB/T 12334-90 Definition and general rules for thickness measurement of metal and other inorganic coatings
40. GB/T 13452.2-92 Colored paints and varnishes Method for determining the thickness of coating films
Gloss
41. GB/T1743-79(89) Method for determining the gloss of coating films
42. GB/T9754-88 Colored paints and varnishes Determination of mirror gloss at 20°, 60°, and 85° for non-metallic pigment coatings
Adhesion
43. GB/T 1720-79(89) Method for determining the adhesion of coating films
44. GB/T 5210-85 Method for determining the adhesion of coatings by pull-off method
45. GB/T 9286-1998 Colored paints and varnishes Crosshatch adhesion test for coating films
- Thickness Detection—Wet Film Gauge
-
The wet film comb, also known as a wet film thickness gauge, thickness gauge, wet film card, is a tool used to measure the thickness of coatings such as paint and varnish during application. After the coating is applied, the wet film thickness gauge is immediately placed vertically and steadily on the surface of the flat-coated object, allowing for an immediate measurement of the coating thickness.
Elcometer Hexagonal Wet Film Comb (Stainless Steel)

The operation is as follows

Made of corrosion-resistant stainless steel, each side has a series of teeth with varying heights. The external reference teeth at both ends are on the same horizontal plane, forming a baseline. The inner teeth arranged along the baseline form a progressive gap series. Each inner tooth is marked with a specified gap depth value. During use, place the comb on a flat sample surface, ensuring the comb teeth are perpendicular to the sample surface. After removing the comb, the maximum gap depth of the wetted inner teeth indicates the wet film thickness. It is a simple and quick tool for measuring the wet film thickness of coatings such as paint and varnish during application.
- Thickness Measurement—Dry Film Gauge
-
Film thickness is an important indicator of the coating. It not only affects the materials, labor, and costs during film formation but also relates to the performance of the coating. Therefore, the testing of coating performance should be conducted at a specified film thickness. After the coating has completely dried, the dry film thickness can be measured according to the national standard GB1764-89(79). The value of the dry film thickness is an important aspect of thickness management. Only when each coating layer reaches the specified dry film thickness can the overall total film thickness requirement be met.
Acceptance criteria specified in ISO 19840:
To be accepted and approved, the film thickness of a test area must meet the following criteria:
1. The arithmetic average of all measurements must be equal to or greater than the rated dry film thickness value;
2. All measurements must be equal to or greater than 80% of the rated dry film thickness value;
3. No more than 20% of the total measurement points should have a measurement below 80% of the rated dry film thickness value but not lower than it;
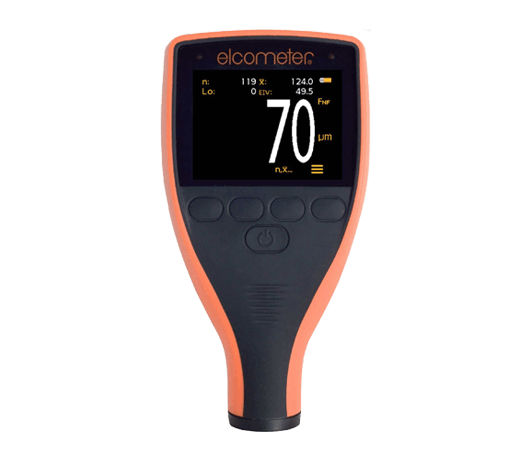
4. All measurements should be equal to or less than the maximum dry film thickness value, as specified in ISO 12944-5 if not otherwise specified.Common model: Elcometer 456 Coating Thickness Gauge
Instructions: The Elcometer 456 coating thickness gauge, manufactured by the British company Elcometer, is suitable for measuring the coating thickness on various metal substrates. It is highly regarded for its excellent performance and practical design. With improved functionality and simplified screen menus, the Elcometer 456 has become one of the most advanced coating thickness gauges in the world. This leading product is available in basic, standard, and advanced models, with both integrated and separate probes. There are many options, and the Elcometer 456 can meet your specific application needs.
- Adhesion Test—Pull-off Tester
-
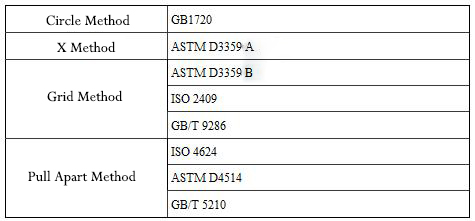
The methods for testing coating adhesion include the circle method, grid method, X method, and pull-off method. Different testing methods correspond to different standards, as shown in Table 1. Among them, the circle method is not suitable for checking the adhesion of coatings on-site but is used for testing coating performance in the laboratory.
The pull-off method is the best test for evaluating adhesion. An aluminum alloy cylinder is glued to the coating surface with an adhesive. Once the adhesive is fully cured, the pull-off method tester is used to test adhesion.

The pull-off method testers come in two types: mechanical and hydraulic/pneumatic-driven. Typical testers include the Elcometer 106 (mechanical) and Elcometer 108 (hydraulic). The Elcometer 106 is a manual mechanical pull-off tester, but due to the instability of manual operation, it can affect the accuracy of the test results, which is why the mechanical pull-off method is no longer used in marine corrosion engineering standards (NORSOK M501).
Specific operation:
The adhesives used in the pull-off adhesion test include two types: epoxy resin adhesive and fast-drying cyanoacrylate adhesive. The epoxy adhesive requires 24 hours at room temperature before testing, while the fast-drying cyanoacrylate adhesive can reach the required test strength after 15 minutes at room temperature, and testing is recommended after 2 hours.
The purpose of the transparent tape is to hold the aluminum alloy cylinder in place, preventing it from shifting before the adhesive has fully cured.
The cutting tool is used to cut the coating and adhesive around the aluminum alloy cylinder until the substrate is reached. This prevents the surrounding coating from affecting the accuracy of the adhesion test. If the dry film thickness is less than 150μm, cutting is not necessary.
For convenience, ISO 4624 defines a series of symbols to describe the condition:
A = Cohesion failure of the substrate
A/B = Adhesion failure between the substrate and the first coat
B = Cohesion failure of the first coat
B/C = Adhesion failure between the first and second coats
n = Cohesion failure of the nth coat in a multi-coat system
n/m = Adhesion failure between the nth and mth coats in a multi-coat system
-/Y = Adhesion failure between the last coat and the adhesive
Y = Cohesion failure of the adhesive
Y/Z = Adhesion failure between the adhesive and the test cylinderAdhesion strength is expressed in N/mm² (MPa). For example, a coating system has a pull-off stress of 20 MPa. If 30% of the coating cohesion failure occurs on the cylinder and the first coat, and 70% of the adhesion failure occurs between the first and second coats, this would be expressed as: 20 MPa, 30% B, 70% B/C.
-
Standard Adhesion Test Values
In NORSOK M501, adhesion tests for organic coatings require the use of an automatic pull-off instrument, not a manual mechanical type. Corrosion protection coatings generally require at least 5.0 MPa. For fireproof coatings, cement-based coatings require 2.0 MPa, while epoxy-based products require 3.0 MPa to be deemed acceptable.
In ISO 12944-6, adhesion for coating systems (when the dry film thickness is greater than 250 microns) must be tested according to the ISO 4624 pull-off method, and the adhesion must be at least 5 MPa.
For the maintenance of old coatings, the reference value must be at least 2 MPa to confirm that the original coating has adequate adhesion to be retained. Otherwise, the old coating should be removed.
For newly constructed structures, the adhesion of corrosion protection coatings to concrete surfaces is generally specified as no less than 1.5 MPa. The GB5210-85 standard refers to the international standard ISO4624-1978, and adhesion is measured in units of kg/cm2.
- Adhesion Test—Cross Cut Method
-
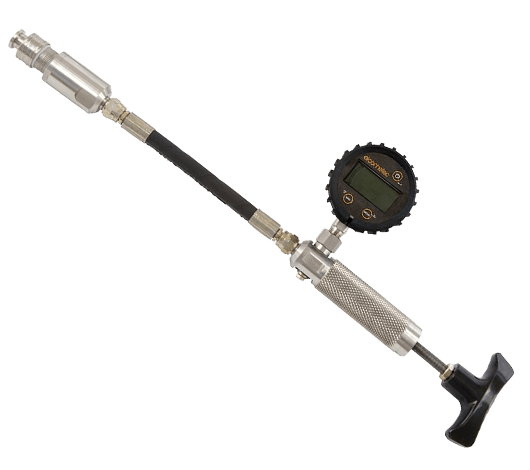
The main standards for the cross cut test are ASTM D3359 Method B and ISO 2409. Both methods and descriptions are quite similar, but the explanation of adhesion levels is in reverse order. ASTM D3359 uses a scale from 5B to 0B, from good to poor, while ISO 2409 uses a scale from 0 to 5, from good to poor. The Chinese National Standard GB/T9286-1998 adopts ISO2409:1992 equivalently.
ISO 2409 Testing Method:
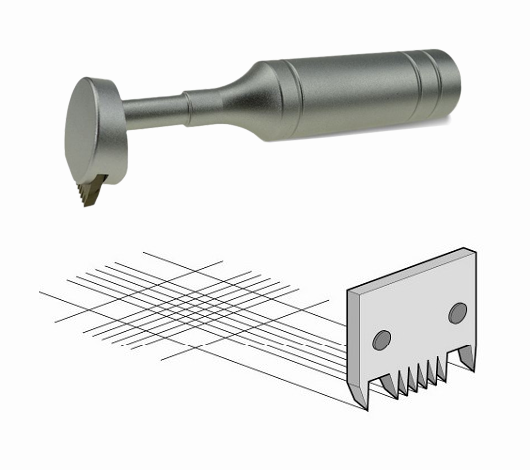
The tools used in ISO 2409 cross cut testing include both multi-blade and single-blade tools. Since multi-blade tools are not easy to cut through the coating film smoothly on substrates with a dry film thickness >120 μm or harder coatings, single-blade tools are recommended. To avoid human error, an electric cross-cut adhesion tester can be used, with adjustable tool pressure. Some equipment manufacturers, such as the German company Erichzen, produce the 430 model, which can conduct various tests such as single-line, multiple-line, star-shaped, and wedge-shaped. Single-blade tools also require instruments with varying spacings.
0 - 60 microns with 1 mm spacing on hard substrates
0 - 60 microns with 2 mm spacing on soft substrates
61 – 120 microns with 2 mm spacing on hard or soft substrates
121 - 250 microns with 3 mm spacing on hard or soft substratesCross Cut Test Procedure:
(1) Measure the film thickness to determine the appropriate cutting spacing.
(2) Cut the coating with stable pressure, appropriate spacing, and at a uniform speed, ensuring each cut reaches the substrate surface.
(3) Repeat the previous operation, cutting the coating again at a 90° angle to form a grid.
(4) Sweep the surface with a soft brush. Apply adhesive tape firmly over the grid, leaving at least 20 mm beyond the grid to handle the tape.
(5) Hold one end of the tape and peel it off at a 60° angle within 0.5-1.0 seconds. Keep the tape as a reference and inspect the cut areas.According to ISO 12944, an adhesion level of 1 is required for the test to be considered acceptable. In GB/T 9286-1998, the first three levels are considered satisfactory, and the pass/fail evaluation is also based on these first three levels.
- Pin Hole Detection—Low Pressure Method
-
When the insulating corrosion protection layer on a metal surface is too thin or has pinholes, the resistance and gap density are very small. When a high voltage is applied, it causes breakdown at the air gaps, creating a spark discharge, which triggers a pulse signal in the alarm circuit. The alarm system then emits an audio-visual warning. This principle is used for detecting leakage in corrosion protection layers.
The spark discharge detector is used to test the construction quality and aging corrosion points of corrosion-resistant coatings on metallic surfaces, such as oil and gas pipelines, cables, enamel, metal storage tanks, inner lining protection, and ship hulls. When a corrosion coating has microholes, air gaps, or other quality issues, the device emits a bright spark and an audible alarm. This device is designed with innovation and ease of use, widely applied in industries such as petroleum, chemicals, rubber, enamel, and power plants.
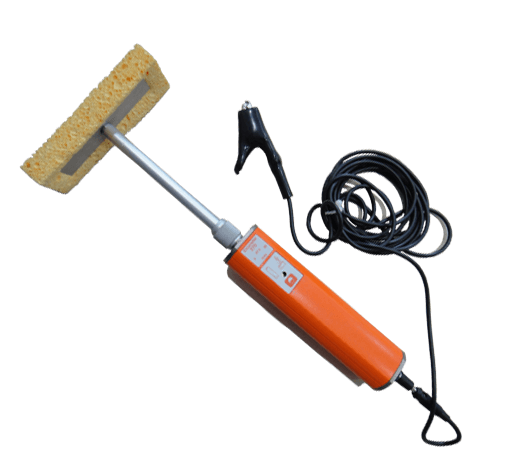

Elcometer 270 Pin Hole Detector
Early corrosion of substrates due to pinholes and cracks in the coating is usually caused by coating failure. One of the main causes of coating failure is the presence of cracks in the coating. These cracks are generally referred to as pores, which can include types such as sagging, flowing, subsidence, pitting, pinholes, excessive coating thickness, and insufficient coating. The Elcometer 270 series uses wet sponge technology, setting a new standard for low-voltage wet sponge detectors with high quality, similar to high-voltage spark discharge detectors.
Testing Steps:
1) Connect one end of the circuit wire to the main unit, and the other end, equipped with a crocodile clip, to the uncoated substrate.
2) Wet the sponge with clean tap water.
3) Keep the sponge clean and turn on the device.
4) After the device is powered on, wait for 4 seconds until you hear two beeps, then the device will automatically calibrate.
5) Choose the appropriate test voltage:
· 9V for coatings with a thickness less than 300 microns (12 mils).
· 90V for coatings with a thickness less than 500 microns (20 mils).
· 67.5V is the US standard.
6) Move the wet sponge across the coating. When it passes over a pinhole, the LED will flash and an alarm sound will be emitted. When the sponge is moved away from the pinhole, the alarm will stop.
7) To precisely locate small pinholes, use the corners of the sponge.
-
-
How to Select the Right Coating Type?
We don't know where to start.
-
ISO 12944 is a standard developed for corrosion protection of steel structures by paints, determining the corrosive environment, anti-corrosion life, paint matching, and film thickness.
Choose
-
How to Solve Industry with Coatings?
Corrosion factors are numerous and varied.
-
We serve municipal engineering, chemical industry, power plants, steel structure factories, and wastewater treatment plants, with numerous successful cases and experience.
Experience
