Construction Steel Structure Anti-Corrosion Solve
The construction industry is one of the pillar industries in China and has become a new growth point driving the country's economic development. Due to the many advantages of steel structures, such as excellent seismic performance, high industrialization, and short construction periods, an increasing number of industrial and civil buildings are adopting steel structures as their load-bearing system. Compared with traditional concrete structures, the comprehensive economic benefits of building steel structures are significant. Additionally, the supporting enclosure systems used with steel structures can provide environmental protection, energy-saving effects, and other benefits. The steel used in the main structure of such buildings can also be reused.



-
 Background
Background -
 Design Basis
Design Basis -
 New Steel Structure Construction Plan
New Steel Structure Construction Plan -
 Steel Structure Renovation Plan
Steel Structure Renovation Plan -
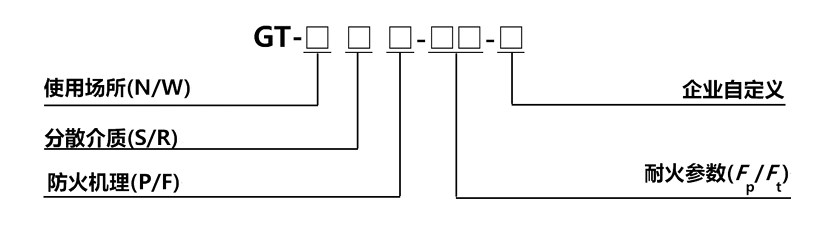
 Steel Structure Fireproof Plan
Steel Structure Fireproof Plan
-
- Corrosion Protection Background for Building Steel Structures
-
I. Background of Anti-corrosion for Building Steel Structures
Municipal public facilities, such as large exhibition centers, sports venues, airport terminals, TV towers, and bridges, all use a large amount of steel as the primary structural form. Steel is an important structural material in modern buildings. It has high strength, stable performance, good toughness, convenient processing, suitability for mass production, easy quality control, and quick installation. Therefore, it is particularly suitable for constructing large-span, super-high, and heavy buildings.
In typical urban environments, factors like car exhaust emissions, sulfur-containing gases from power plants and boiler chimneys, industrial air pollution in industrial cities, and salt mist erosion in coastal cities, as well as humid heat in southern cities, inevitably lead to corrosion of steel structures. The use of anti-corrosion coatings to protect steel structures in municipal public facilities is an economically feasible method, and a suitable coating system can achieve durability of more than 25 years.
Apart from considering corrosion protection, another key coating to consider is fire protection, as the fire resistance of building steel structures is relatively poor. This manifests in two aspects: first, the high thermal conductivity of steel leads to quick temperature rise during a fire; second, the strength of steel decreases rapidly as the temperature increases, causing the steel structure to collapse under external loads. The main goal of fire protection for building steel structures is to ensure enough escape time during a fire. Therefore, to prevent and reduce the fire hazards of building steel structures, scientific fire protection design and reliable, economical fire protection measures must be adopted.
In the application of anti-corrosion and fireproof coatings for steel structures in municipal public facilities, long-term durability, aesthetic decoration, and environmental protection must all be taken into account. Heavy-duty anti-corrosion and fireproof coatings used for building steel structures should reflect the best combination of performance, aesthetics, and environmental regulations.

II. Corrosive Media in Building Steel Structures
The corrosive media that building steel structures face mainly include:
1. Moisture in the Atmosphere
In urban environments, the air humidity is relatively high, especially in cities near rivers, lakes, or the sea. The moisture in the air forms a water film on the steel structure's surface, accelerating the corrosion process.
2. Oxygen in the Atmosphere
Oxygen is a key factor in causing steel oxidation reactions. It combines with moisture on the steel surface to form corrosive electrolytes.
3. Air Pollution
In cities, industrial emissions, car exhausts, and pollutants contain sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other acidic gases, which dissolve and exacerbate the corrosion of steel structures.
4. Dust and Particles
Dust and particles in cities can adhere to the steel structure's surface. These substances may contain corrosive components, accelerating the corrosion process.
5. Salt
Steel structures in coastal cities are also affected by salt mist. Salt in seawater (mainly sodium chloride NaCl) is highly corrosive and can accelerate the corrosion rate of metal.
6. Microorganisms
In humid environments, microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi may also participate in the corrosion process, especially in warm and humid climates.
7. Chemicals
Certain chemicals in urban areas, such as detergents and antifreeze, may come into contact with steel structures. The components of these chemicals can promote corrosion.
8. Temperature Changes
Temperature differences in cities also affect steel structures. Particularly with large temperature variations between day and night, temperature changes lead to condensation on the surface of the steel structure, accelerating corrosion.
9. Industrial Emissions
Steel structures in industrial areas are also affected by specific industrial emissions such as acidic gases and heavy metal ions.
To address the impact of these corrosive media, urban steel structures typically require effective anti-corrosion measures, such as high-performance coatings, cathodic protection systems, and the use of corrosion-resistant alloys to ensure the structure's durability and safety.
-
How to Select the Right Coating Type?
We don't know where to start.
-
ISO 12944 is a standard developed for corrosion protection of steel structures by paints, determining the corrosive environment, anti-corrosion life, paint matching, and film thickness.
Choose
-
How to Solve Industry with Coatings?
Corrosion factors are numerous and varied.
-
We serve municipal engineering, chemical industry, power plants, steel structure factories, and wastewater treatment plants, with numerous successful cases and experience.
Experience